The steps for determining your computer's Media Access Control (MAC) address will vary depending on what operating system you are running on your computer. Please see the steps below for obtaining your MAC address for
Windows and
MAC OS X.
1. Press the  (Win+R keys) simultaneously to bring up the Run Command
(Win+R keys) simultaneously to bring up the Run Command
2. Type cmd and press Enter to bring up a Command Prompt window.

3. At the command prompt, type: getmac and then press Enter

4. The MAC Address is noted as the Physical Address in the command prompt window. An example of a MAC Address would be: 00:0a:95:9d:68:16

1. From the
Apple menu, select
System Preferences. In System Preferences, from the View menu, select
Network.


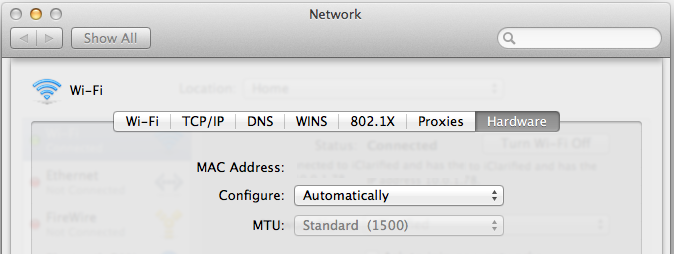
2. In the
Network preference window, click a network port (e.g., Ethernet, AirPort, Wi-Fi)
3. From the list of interfaces, select
either Wi-Fi or Ethernet (whichever is being used)


4. After selecting the desired interface, click on the
Hardware tab
5. The current MAC Address for the selected interface will be displayed. An example of a MAC Address would be: 00:0a:95:9d:68:16
 Note:
Note: Advanced Mac OS X users can also find the MAC Address using the Terminal using the steps below:
1. Open a
Terminal Window
2. Use the
ifconfig command from a
Terminal window to display the current network configuration
4. Typically an
en0 connection will be your Ethernet connection and
en1 will be wireless. If only a wireless connection is being used then
en0 will be that specific connection. The MAC address will be preceded by the word
ether before the MAC Address for both Ethernet and wireless connections
Need additional help? Access 24/7 live chat, create a case from your
My ASU Service Center or call 855-278-5080.



